SQL Server Configuration
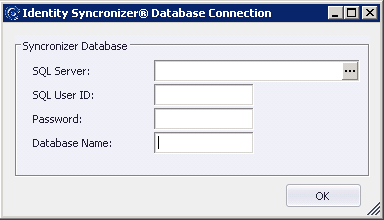
When the Identity Syncronizer® Management studio is run for the first time, it will look for the SQL Server connection Settings. If these settings need to be set, a pop-up window will be displayed for you to fill in the required fields (SQL Server IP address or name and instance, SQL Server User ID and password, and, database name).
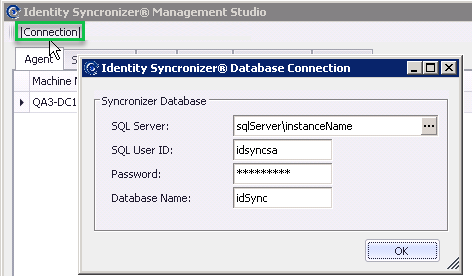
If you then need to change any of those settings, open the Identity Syncronizer® Management Studio and click on on the 'Connection' button (top-left corner of the Management Studio), to open the 'Database Connection' window:
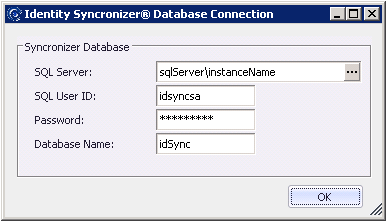
Enter the necessary SQL Server Information in the dialog above.
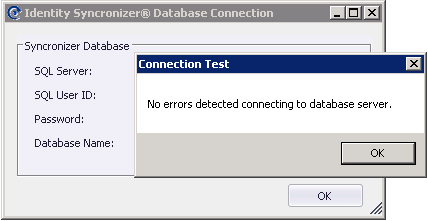
Once the SQL connection data has been set, click on the ellipses ([...]) button to test the connection. If the connection is successful , close the Test-window and then click on the "OK" button to save the SQL Server Connection configuration.
Tips :
- Do not use "localhost" to refer to the SQL Server location. Either use the hostname or IP Address to refer to the SQL Server host.
- Identity Syncronizer® uses a SQL server user name and password combination, so Mixed mode Authentication needs to be enabled.
- Identity Syncronizer® also communicates with SQL server via TCP/IP and Named Pipes, so these protocols need to be enabled.
- Identity Syncronizer® uses the SQL Server Browser service, so ensure that it is enabled and started.
- The database specified in the "Database Name" field will be automatically created by Identity Syncronizer, so the SQL Server User specified in this configuration screen needs to have permissions to create databases on the SQL server.
- Initially, the SQL User needs to have sysadmin rights in order to create the database. After the database has been created, the SQL User needs the db_owner role to operate without problems (the sysadmin role may be then removed from its security profile)